Wired Memory on Mac is a vital part of Mac’s memory configuration, is that portion of the system’s RAM reserved for storing crucial data.
Have you ever wondered what
wired memory on Mac is and why it’s important? If so, you’re not alone. Wired memory, often known as
resident memory, is crucial to the smooth operation of your
macOS.
In this article, we will demystify wired memory in detail to help you understand its role in
system performance and
optimization techniques for better
computer efficiency. Dive into the nitty-gritty of Mac’s
memory management with us!
Quick Summary
- Wired memory on a Mac refers to the portion of RAM reserved for essential data needed by the macOS kernel and its associated data structures.
- Unlike other types of memory, wired memory cannot be swapped or paged out to disk storage under any condition.
- Monitoring wired memory usage in Activity Monitor can help you understand how much memory critical processes use and optimize your Mac’s overall performance.
- To manage high-wired memory, regularly update your macOS software, close unnecessary applications, and reduce the number of open tabs in web browsers.
- Optimizing wired memory usage involves managing background processes, limiting startup items, updating software regularly, using Activity Monitor to monitor resource-intensive processes, adjusting virtual memory settings if necessary, and clearing cache files periodically with caution.
Understanding Wired Memory on Mac
To fully comprehend the concept of wired memory on your Mac, it is essential to grasp its definition and purpose.
Definition of wired memory
Wired memory, a vital part of your Mac’s memory configuration, is that portion of the system’s RAM
reserved for storing crucial data needed by the
macOS kernel and its associated data structures.
This type of memory
cannot be swapped or paged out to disk storage under any condition due to its importance. It
holds critical information like
virtual memory objects related to core functions and software operations on your Macbook.
The key characteristic distinguishing wired memory from other types of memory in your MacBook is its
immediate accessibility, ensuring swift performance for your system activities.
Purpose of wired memory
Wired memory on your Mac is crucial in ensuring
smooth and efficient performance. It is a memory
reserved exclusively for the macOS kernel and its essential data structures.
In other words, it
contains important background information related to the core functions of your computer’s operating system.
This wired memory also plays a role in storing data for virtual memory objects. These are pieces of information that applications or the system need immediate access to and, therefore, cannot be cached to disk.
Think of wired memory as the
fast-access storage area where critical information resides, allowing your Macbook to retrieve and process necessary data quickly.
Difference between wired memory and other types of memory
Understanding the difference between wired memory and other types of memory in your Mac is key to optimizing its performance.
Here’s a simple table to help you distinguish between these types of memory:
| Memory Type |
Description |
Why It’s Important |
| Wired Memory |
Memory that cannot be swapped out to disk is often reserved for the macOS kernel and its data structures. |
Ensures quick access to important system operations, preventing lags or freezes. It cannot be cached to disk, ensuring constant availability. |
| Active Memory |
Open applications and processes are currently using memory. |
Keeps your active apps running smoothly and promptly. The more active memory, the faster your applications can run. |
| Inactive Memory |
Memory that holds data from recently closed applications, allowing for quicker reopening should you need them again. |
Improves efficiency by speeding up the reopening of recently closed applications. Inactive memory can be reassigned to other processes if needed. |
| Free Memory |
Memory that is currently not being used. |
Maintains system performance. If your Mac runs out of active, wired memory, it will use free memory. |
Monitoring these memory types on your Mac is essential to ensure optimal performance. The
Activity Monitor on your Mac provides a real-time snapshot of your system’s memory usage.
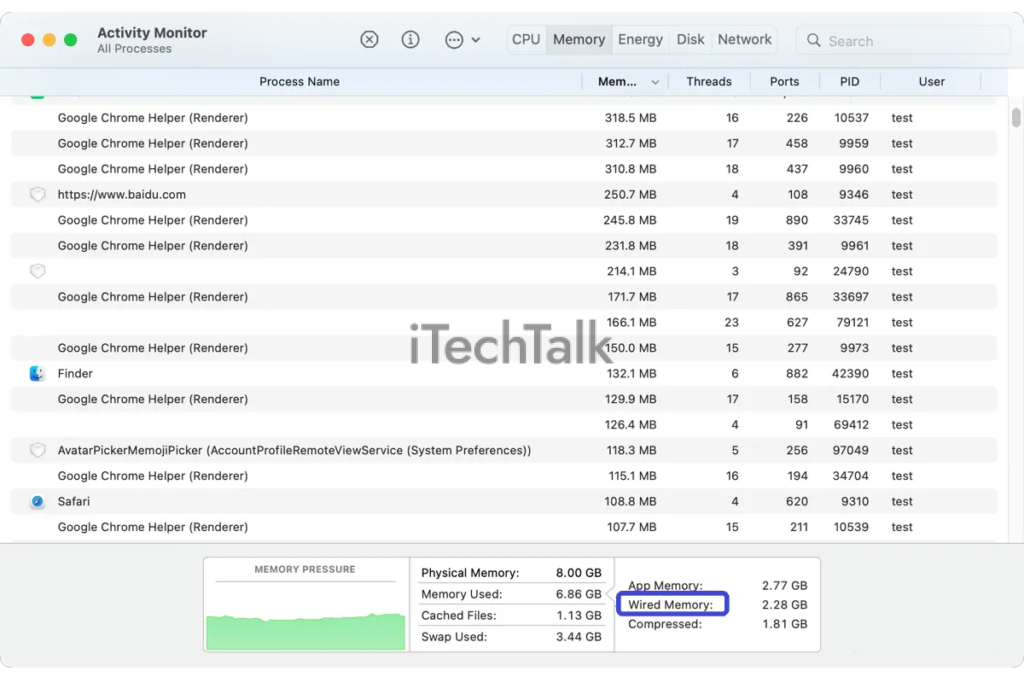
Checking Wired Memory on Mac
To check the wired memory usage on your Mac, you can view it through the Activity Monitor application or by using the zprint terminal command.
How to view wired memory usage
To view wired memory usage on your Mac, follow these steps:
- Open the Activity Monitor application. You can find it by going to the “Applications” folder or searching for it using Spotlight (press Command + Space and type “Activity Monitor”).
- Click the “Memory” tab at the top in the Activity Monitor window. This will display information about your Mac’s memory usage.
- Look for the “Wired” category under the “Memory Pressure” section. Wired memory is displayed as a blue bar in the graph and as a numerical value next to it.
- The numerical value represents the amount of memory currently being used by wired processes. A higher number indicates that more wired memory is being used.
- You can also hover your mouse over the blue bar to get a tooltip that shows the exact amount of wired memory in gigabytes (GB).
Interpreting wired memory data
To make the most of your Mac’s performance, it’s important to understand how to interpret
wired memory data. Wired memory, or
resident memory, consists of crucial information that the
macOS kernel and its data structures require for seamless operation.
This includes virtual memory objects and
essential background details related to the software, kernel code, and core functions of your Mac.
Unlike other types of memory, wired memory
cannot be swapped out or cached to disk—it needs immediate access for smooth functioning.
Interpreting wired memory usage is relatively easy with the right tools. You can use commands like “zprint” in
Terminal to print detailed information about your Mac’s wired memory.
Additionally, you can check RAM usage using Activity Monitor or by clicking on the Apple menu and selecting “About This Mac.”
By understanding the nuances of wired memory data and monitoring its utilization, you can optimize your Mac’s performance and ensure efficient functionality without unnecessary jargon or fluff.
Managing Wired Memory on Mac
To manage wired memory on your Mac, you can optimize its usage by following these tips and clearing any unnecessary wired memory.
Why wired memory may be high
If you find that the wired memory on your Mac is high, it could be due to a few reasons. One possibility is that certain applications or processes request a large amount of memory that must be immediately accessible.
This can include
system services or background tasks running in the kernel code. Another reason for high wired memory usage could be related to virtual memory objects or data structures essential for macOS’ smooth operation.
You can follow a few tips to optimize your Mac’s performance and manage high-wired memory. First, ensure you’re regularly updating your macOS software, as newer versions often come with improvements in memory management.

Additionally,
closing unnecessary applications and reducing the number of open tabs in web browsers can free up some wired memory.
If you’re experiencing persistent issues with high-wired memory, consider contacting Apple support or consulting their documentation for more detailed troubleshooting steps.
Tips for optimizing wired memory usage
To ensure optimal performance on your Mac, it’s essential to optimize the usage of wired memory.
Here are some tips to help you make the most out of this crucial component of your Mac’s memory system:
- Manage background processes: Close any unnecessary applications or processes running in the background. These might be using valuable wired memory resources, affecting overall system performance.
- Limit startup items: Reduce the number of applications automatically launching at startup. By doing so, you can prevent them from consuming wired memory right from the beginning.
- Update software regularly: Keeping your macOS and applications up to date can help minimize memory-related issues. Software updates often include optimizations that improve memory management and efficiency.
- Use Activity Monitor: Launch the Activity Monitor utility (found in the Utilities folder within Applications) to identify resource-intensive processes or applications. Monitoring their resource usage can provide insights into potential memory optimization opportunities.
- Adjust virtual memory settings: Virtual memory is a technique used by macOS to supplement physical RAM with disk space when needed. Adjusting virtual memory settings allows you to fine-tune its allocation and optimize wired memory usage.
- Clearing cache files: Periodically clearing cached files can free up some wired memory space. However, exercise caution as clearing certain caches may temporarily impact application performance until they are rebuilt.
- Upgrade RAM: If your Mac consistently runs out of available wired memory, consider upgrading your RAM (Random Access Memory). Increasing the installed RAM can provide more headroom for wired and other memory usage.
Clearing unnecessary wired memory
To optimize the performance of your Mac and free up valuable resources, it’s important to clear unnecessary wired memory.
Here are some steps you can take:
- Identify memory-hogging applications: Use the Activity Monitor application to identify applications that consume a significant amount of wired memory. Look for processes with high memory usage and consider closing them if they’re not essential.
- Restart your Mac: A simple restart can sometimes help clear out unnecessary wired memory. This allows the system to start fresh and reallocate resources more efficiently.
- Update your software: Keeping your macOS and applications up to date ensures that you have the latest bug fixes and optimizations, which can help improve memory management.
- Disable automatic startup processes: Some applications may automatically launch during startup, consuming valuable resources from the beginning. Go to “System Preferences > Users & Groups > Login Items” and remove any unnecessary applications from the list.
- Clear caches: Caches are temporary files applications create to speed up performance. However, these caches can accumulate over time and take up valuable space in wired memory. You can use third-party tools like CleanMyMac or Onyx to remove unnecessary caches.
- Limit open applications and tabs: Having multiple applications and browser tabs open simultaneously consumes more memory, including wired memory. Close unused applications and tabs to free up resources.
- Manage login items: Review the list of applications that open at login by going to “System Preferences > Users & Groups > Login Items”. Remove unnecessary applications from the list to prevent them from consuming wired memory on startup.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wired memory on a Mac refers to the memory reserved for the macOS kernel and its essential data structures. It is crucial in ensuring
immediate access to important system functions and
cannot be swapped or cached to disk.
Understanding how wired memory works can help
optimize performance and ensure
efficient memory management on your Mac. So, dive into your
Activity Monitor and take control of your Mac’s wired memory for a smoother
computing experience!
 Additionally, closing unnecessary applications and reducing the number of open tabs in web browsers can free up some wired memory.
If you’re experiencing persistent issues with high-wired memory, consider contacting Apple support or consulting their documentation for more detailed troubleshooting steps.
Additionally, closing unnecessary applications and reducing the number of open tabs in web browsers can free up some wired memory.
If you’re experiencing persistent issues with high-wired memory, consider contacting Apple support or consulting their documentation for more detailed troubleshooting steps.
 Here are some steps you can take:
Here are some steps you can take: